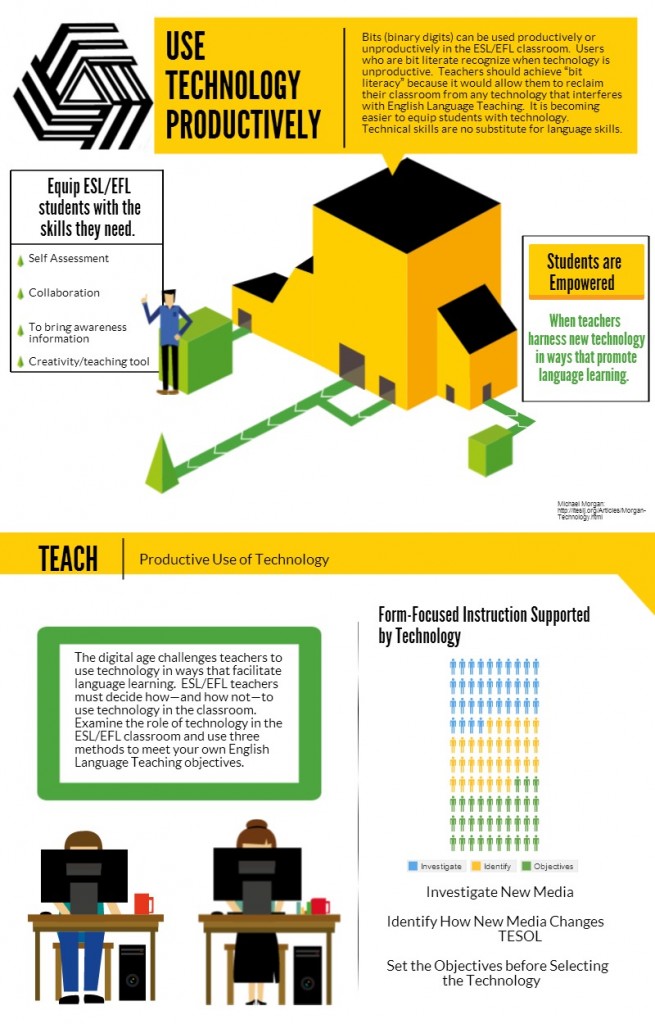
In today’s digital age, technology is an essential component of the English as a Second Language (ESL) and English as a Foreign Language (EFL) classroom. However, simply incorporating technology is not enough. For technology to genuinely enhance learning, teachers and students must become “bit literate.” Bit literacy is the practice of efficiently managing digital information by investigating, identifying, and setting clear learning objectives to make the use of technology more productive.
This article will explore the concept of bit literacy and offer practical strategies for TESOL teachers to empower their students to learn more effectively in a technology-rich environment.
What is Bit Literacy?
Bit literacy involves the ability to manage, understand, and utilize digital information (or “bits”) in a purposeful and organized manner. In the context of ESL/EFL teaching, it means going beyond merely using technology for its own sake. Instead, it requires intentional use of digital tools and resources to enhance language learning. Bit literacy encourages both teachers and students to think critically about the purpose of each digital tool, how it fits within the learning objectives, and how to effectively manage the influx of digital content that can overwhelm the learning process.
Investigating the Role of Technology in the Classroom
The first step towards bit literacy is investigating the role of technology in the classroom. Not every digital tool or app is suitable for every learning objective, so it is essential to understand the “why” behind using a specific tool. Consider these factors when evaluating the role of technology in ESL/EFL learning:
- Learning Outcomes Alignment: Does the tool align with the learning objectives? For example, if the goal is to improve students’ listening skills, tools such as language podcasts or voice recording apps may be more suitable than a grammar-based game. Identify how each tool contributes to meeting specific language goals.
- Engagement and Motivation: Is the technology engaging and motivating for students? Digital tools should not only be functional but also capture students’ interest. A tool like a digital storytelling app can motivate students to practice writing and speaking skills in an enjoyable way.
- Ease of Use: Is the tool user-friendly and accessible for all students? If students spend more time figuring out how to use a tool than engaging in language practice, it may not be the right choice. Choose tools that match students’ technological proficiency and language level.
Identifying Clear Learning Objectives
Setting clear learning objectives is a fundamental aspect of bit literacy. It ensures that the use of technology in the ESL/EFL classroom is driven by specific educational goals rather than a vague desire to be “innovative.” Learning objectives should be SMART: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. Here are some ways to set clear learning objectives when using technology:
- Break Down Learning Goals into Manageable Tasks: Instead of broad objectives like “improve vocabulary,” focus on smaller goals such as “learn and use 10 new words related to travel by the end of the week.” Use digital flashcards or language learning apps to reinforce the vocabulary.
- Integrate Technology with Traditional Methods: Aim for blended learning where technology complements traditional methods. For example, use online discussion forums for students to extend class debates or record pronunciation practice via a voice recognition app that provides feedback.
- Focus on Process Over Product: When setting objectives, emphasize the process of learning. For instance, if using a digital tool for writing, the objective could be to draft, peer review, and revise a written piece rather than solely submitting a final version. This approach helps students see technology as a part of the learning process, not just a means to an end.
Making Productive Use of Technology
Once clear objectives are set, the next step is to ensure that technology is used productively in the classroom. Here are some strategies to help TESOL teachers make the most out of digital tools:
- Encourage Student-Centered Learning: Technology can facilitate student-centered learning by giving students more control over their learning process. For instance, language apps that allow learners to choose specific modules or topics to study can cater to individual interests and needs. This personalization can motivate students to take ownership of their learning.
- Leverage Collaboration Tools: Utilize tools like Google Docs, Padlet, or Zoom to promote collaboration among students. These tools can be used for group projects, peer editing, and discussions. Collaborative tasks can enhance speaking, writing, and critical thinking skills while making the use of technology an interactive experience.
- Manage Digital Information Effectively: Teach students to organize and manage digital resources. For example, show students how to use bookmarks, digital folders, or apps like Evernote for organizing their language learning materials. This helps avoid digital clutter and allows students to easily access learning resources when needed.
- Monitor and Adjust Use Based on Feedback: Regularly collect feedback from students on the effectiveness of digital tools. This can be done through quick surveys or informal discussions about which activities they found helpful. Use this feedback to adjust technology use in the classroom. If a certain app or platform isn’t contributing to learning as expected, don’t be afraid to switch to a different tool.
- Emphasize Digital Safety and Etiquette: With increased technology use comes the need for digital safety education. Teach students how to identify credible sources online, protect their privacy, and follow netiquette rules in online interactions. This not only aids language learning but also equips students with essential 21st-century skills.
Apps and Tools to Foster Bit Literacy
To effectively integrate technology into the ESL/EFL classroom, teachers should explore a variety of apps and tools that support bit literacy. Here are some recommended options:
- Quizlet: Ideal for vocabulary practice, Quizlet allows students to create and share flashcards. It also offers gamified learning modes that engage students in studying new words.
- Flipgrid: This video discussion platform encourages students to record their spoken responses to prompts. It’s a great tool for improving speaking skills and practicing pronunciation.
- Grammarly: A writing assistant tool that can help students self-correct their written work. It highlights grammatical errors and provides explanations, which can reinforce grammar rules.
- Edmodo: A classroom management tool that enables teachers to create assignments, quizzes, and facilitate class discussions. It helps in organizing learning materials and tracking student progress.
- Padlet: An interactive platform where students can post responses, images, videos, or web links. It’s perfect for collaborative tasks, brainstorming sessions, or digital storytelling.
The Benefits of Bit Literacy for ESL/EFL Learners
By practicing bit literacy, students develop essential skills that go beyond language acquisition. They learn how to filter information, make informed decisions about the tools they use, and become more independent learners. For TESOL teachers, fostering bit literacy can help create a dynamic and effective learning environment where technology plays a meaningful role in language education.
Conclusion
Incorporating bit literacy into the ESL/EFL classroom involves much more than just using digital tools; it requires a deliberate approach to how technology is integrated into the learning process. By investigating the role of technology, setting clear learning objectives, and making productive use of digital resources, TESOL teachers can empower students to become more efficient, organized, and engaged learners. With the right strategies, technology can not only support language learning but also prepare students to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Embrace the concept of bit literacy, and make the ESL/EFL classroom a space where technology truly enhances the learning experience.