Mastering ESL Communication with the Meta Model
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) offers a wide range of techniques aimed at improving communication, personal development, and teaching efficacy. One of its most influential linguistic frameworks is the Meta Model, a tool designed to clarify meaning by addressing vague, distorted, or incomplete language patterns. For TESOL (Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages) educators, incorporating the Meta Model into lessons can significantly improve students’ clarity of thought and speech, as well as sharpen critical thinking.
1. What Is the Meta Model in NLP?
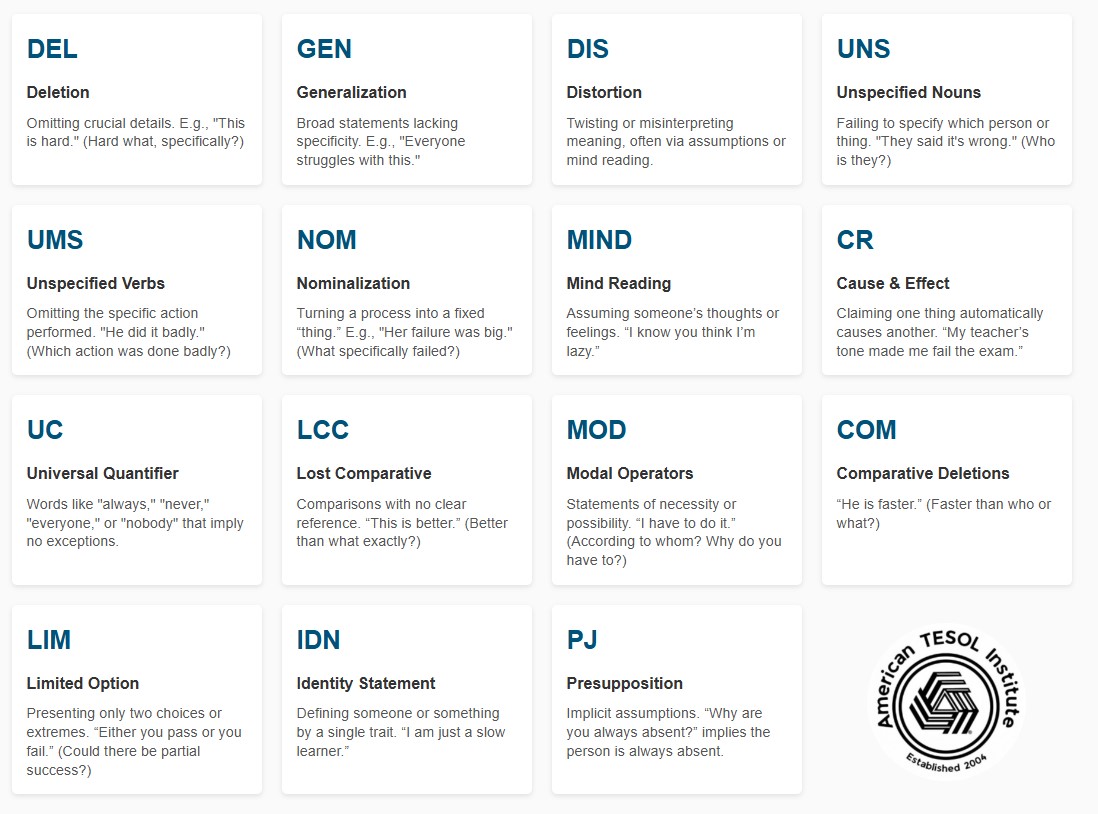
Developed by John Grinder and Richard Bandler (the co-founders of NLP), the Meta Model is essentially a set of probing questions used to challenge and clarify statements. It focuses on identifying three main language distortions:
- Deletions: When essential details or references are omitted.
- Generalizations: Broad statements that lump together multiple experiences or events.
- Distortions: Reinterpretation or skewing of meaning, often via assumptions or mind reading.
By asking targeted questions to uncover missing specifics, educators and students can remove ambiguity, discover hidden assumptions, and achieve clearer, more precise communication.
2. Why Does It Matter for TESOL?
- Clarity of Expression: Many ESL learners struggle with explicit communication. Meta Model questions encourage specificity, helping them articulate exactly what they mean.
- Critical Thinking: Vague language can mask unclear thinking. By challenging generalized or incomplete statements, educators help students strengthen logical reasoning and problem-solving skills.
- Expanded Vocabulary & Syntax: Pushing for detail motivates learners to seek more precise words or structures, boosting their language repertoire.
- Cultural Awareness: Some languages rely on indirect communication. The Meta Model respects this while guiding students to adapt to the more direct style often expected in English contexts.
3. Core Language Patterns and Questions
Here are common language patterns the Meta Model addresses, plus questions to prompt clarity:
Student Statement: “This is difficult.”
Teacher Question: “Which part is difficult? The vocabulary or the instructions?”
Result: Student clarifies, e.g., “The new phrasal verbs confuse me.”
Student Statement: “Everyone hates this homework.”
Teacher Question: “Who specifically hates it? Did others mention they dislike it?”
Result: Student narrows it to, e.g., “Two classmates said they had trouble finishing on time.”
Student Statement: “I know the teacher thinks I’m lazy.”
Teacher Question: “How do you know the teacher thinks that? Did they say it explicitly?”
Result: Student realizes it’s an assumption and revises the statement.
4. Practical Applications in ESL Lessons
Here’s how TESOL teachers can incorporate Meta Model strategies into everyday class activities:
A. Meta Model Drills (Conversational Practice)- Setup: In pairs, students receive cards with vague statements (e.g., “It’s too hard.”).
- Task: One student reads the card; the other uses meta-model questions to clarify details.
- Objective: Engage students in identifying deletions, generalizations, or distortions.
- Setup: Provide scenario cards for common ESL interactions (complaints, test reviews, cultural discussions).
- Task: Students role-play while the “listener” clarifies ambiguities using meta-model questions.
- Objective: Enhance speaking/listening skills in authentic situations.
- Setup: Supply short, vague sentences—e.g., “I felt sad.”
- Task: Students answer meta-model style prompts: Why? Who was involved?
- Objective: Improve descriptive writing and clarity.
- Setup: During grammar lessons, ask meta-model questions if a student says, “I don’t get conditionals.”
- Task: Encourage them to specify what’s confusing—form, meaning, usage, etc.
- Objective: Streamline focus to address exact problem areas in grammar understanding.
5. Teaching Tips for Success
- Model It: Demonstrate first by clarifying an ambiguous statement yourself.
- Embed Gradually: Weave meta-model questions into normal feedback rather than dedicating entire lessons to it.
- Respect Culture: Use the approach sensitively, especially in cultures where direct questioning might feel uncomfortable.
- Encourage Reflection: Let students note how clarifying statements helps them find new vocabulary or grammar forms.
- Keep It Fun: Turn clarifications into collaborative problem-solving, not interrogation.
Incorporating the Meta Model in TESOL classrooms fosters precision, critical thinking, and confidence among ESL learners. By actively questioning vague or incomplete statements, teachers guide students toward refined language use, bridging cultural communication differences and building stronger ESL competencies. For further NLP-based tools that can enhance your teaching approach, visit Meta Model Periodic Table .
Empowering ESL Communication
American TESOL Certification
Mastering the Meta Model is just one of many strategies included in comprehensive TESOL training. By earning a certification through American TESOL Institute, you gain access to a broad set of pedagogical tools for teaching English effectively—both in the classroom and online. Expand your skill set, connect with a global community of educators, and transform your teaching approach with advanced NLP techniques.